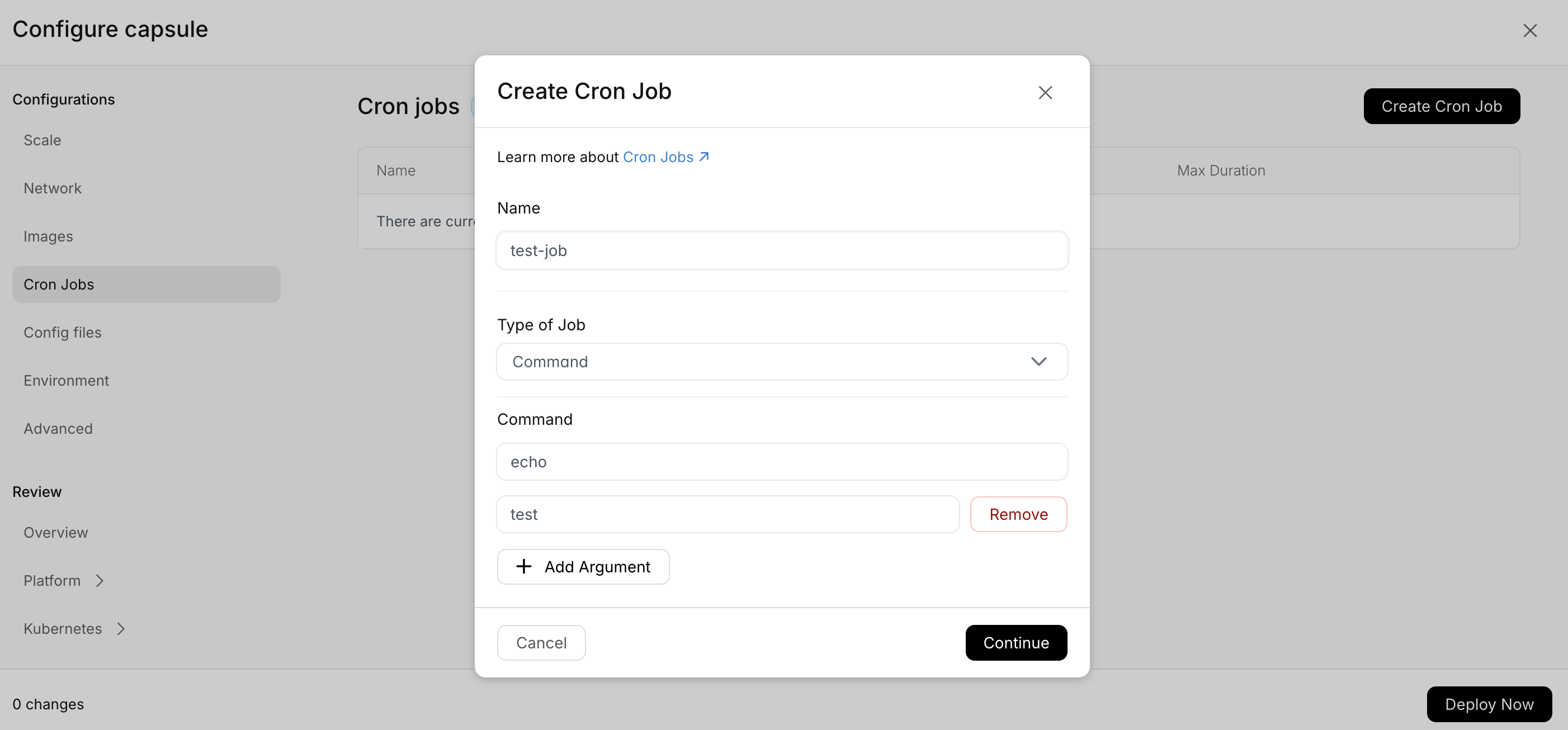
Cron Jobs
You can attach cron jobs to a capsule to execute jobs at a user-defined schedule. We support two different kinds of jobs, bash jobs and http jobs. A bash job spins up a new instance of your capsule whenever it needs to execute a job, runs a job-defined command and then stops the instance. These are good for longer running jobs.
If a job is expected to be quite short-lived, an HTTP job can be used as well. An HTTP job sends a user-defined HTTP request to an existing instance of the capsule. As these jobs are executed entirely within a single HTTP request, they should be able to finish within about a minute.
Retries and Timeouts
A bash job will be retried if the instance exits with a non-zero exit code and an HTTP job will be retried if it returns a non 2xx status code. You can specify the maximum number of retries, which defaults to 6 (same as for Kubernetes Jobs).
You can also specify a max total duration. This limits how long a job execution can live (including all retries) until being terminated. If no max duration is specified, a job execution can potentially run indefinitely if it never exits. In this case, multiple job executions for the same job can run concurrently.
Adding an Viewing Jobs
Jobs can be added either through the CLI or the Dashboard
- Dashboard
- CLI

rig capsule jobs add
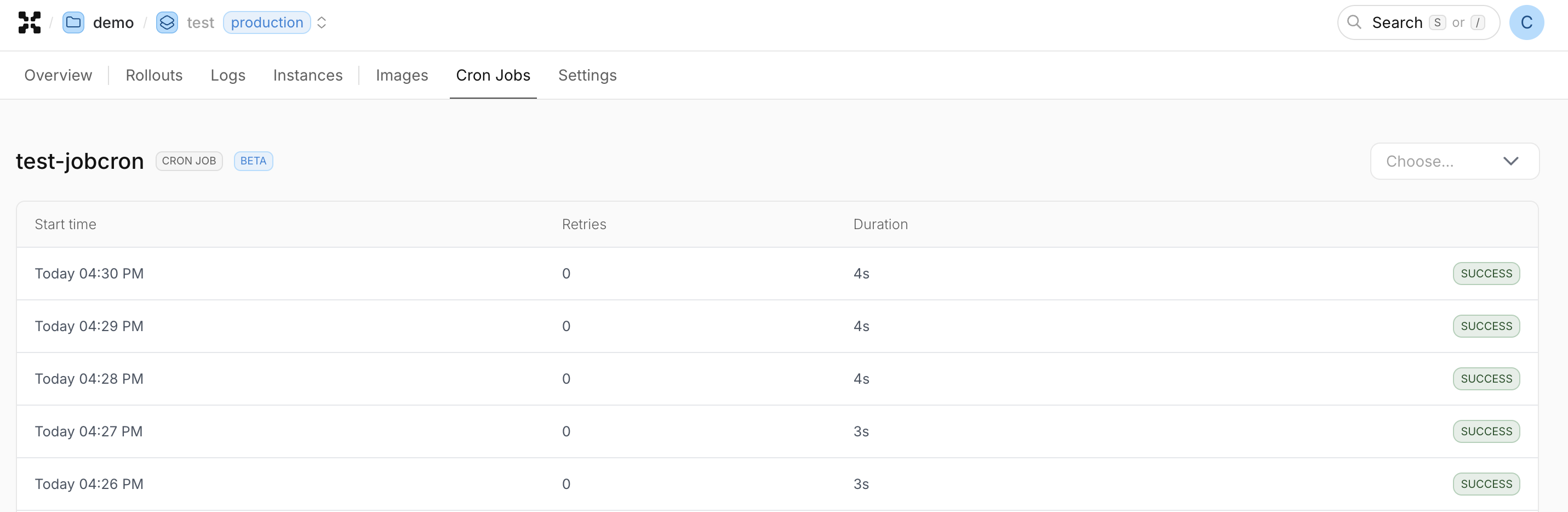
and a history of past executions can be viewed
- Dashboard
- CLI

rig capsule jobs add
Under The Hood
Under the hood, the Rig operator spawns Kubernetes CronJobs which in turn spawns Jobs. For bash jobs, the spawned Job is an instance of your Capsule, and for HTTP jobs it's a lightweight pod using curl to make a request to your capsule.