Rollouts
Whenever you do any change to a Capsule, it will happen as a Rollout of a new configuration. A Rollout is thus the operation of deploying and running a given configuration of the Capsule. When a change is made, e.g. the number of replicas is changed, a new Rollout is automatically initiated, succeeding the currently running.
This Rollout will run until it's being replace by a new one.
Stages
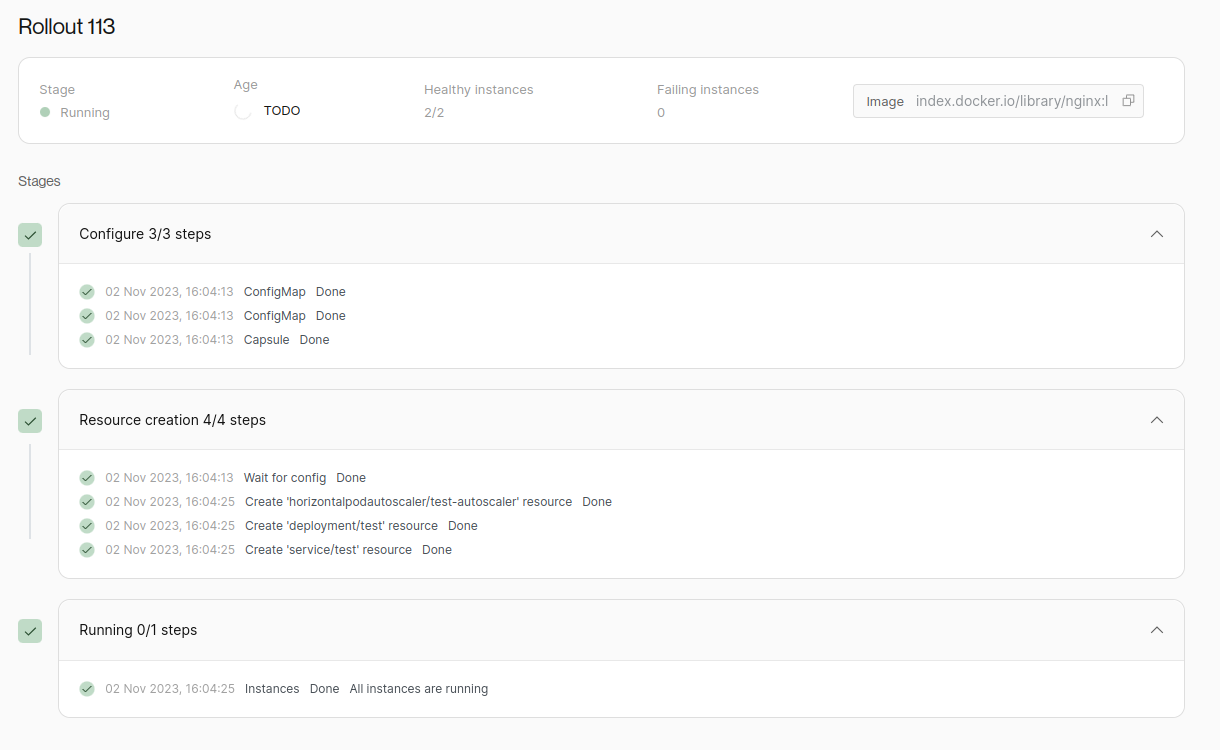
A Rollout has 3 basic stages in its lifecycle:
- Configuration: In this stage, the new resources for the Capsule is generated and being applied. In the basic setup, that means writing it directly to Kubernetes. In a GitOps setup, this is where the new files are written and committed to Git.
- Creating resources: This stage stars when the new resources has been written to Kubernetes. From here a number of Operator-generated resources is further created.
- Running: When all resources are created, the Running stage starts. This tracks the health of the Capsule in the cluster, with initially ensuring all instances are being upgraded.
- Dashboard

Immutability
All Rollouts captures the full configuration, meaning Rollouts serves as an immutable historic view of all changes made to the system, including the resources written to Kubernetes.
Rollbacks
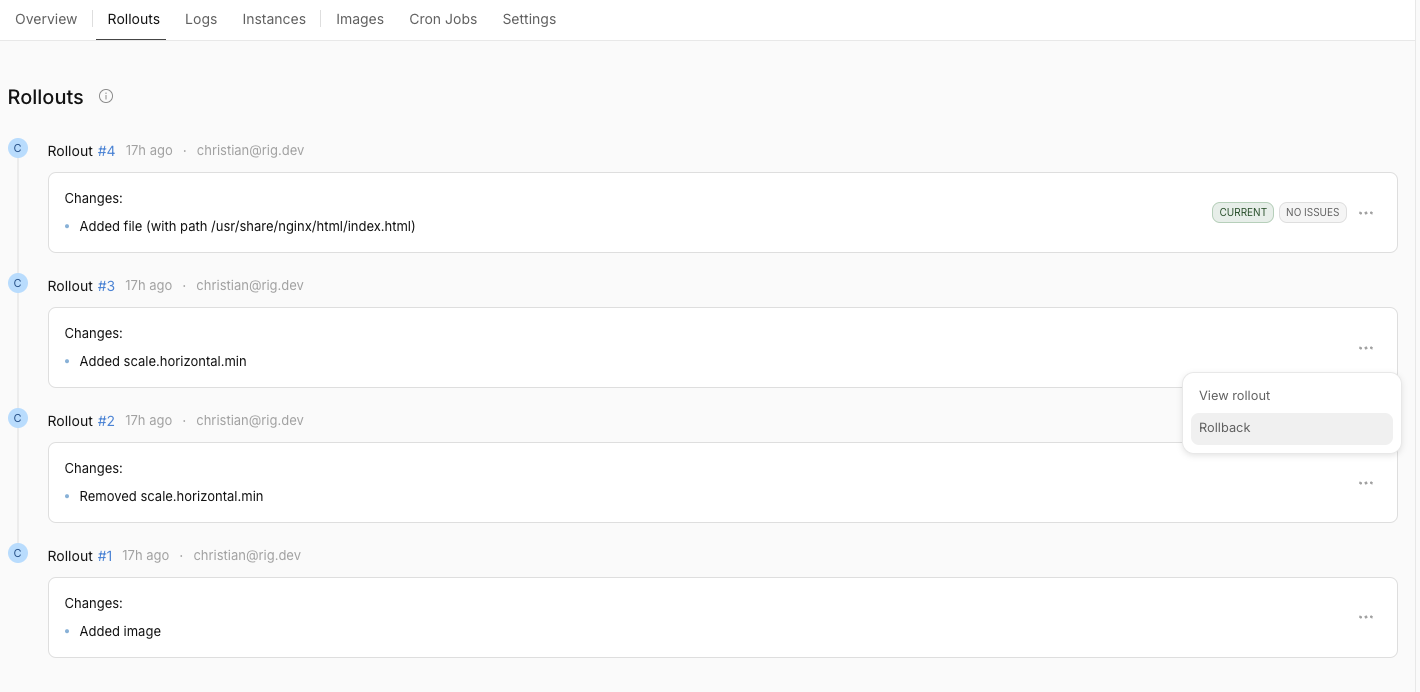
Due to the immutable nature of Rollouts, they naturally work as Rollback points for reverting changes made to the system.
To perform a Rollback to a previous version, simply select the Rollout in question and click Rollback. Because changes only can happen as a Rollouts, the Rollback itself will happen as a new Rollout.
- Dashboard
- CLI

rig capsule rollout rollback <capsule-name> <rollout-id>
Automatic Rollbacks
When deploying using the Rig CLI, you can enable automatic Rollbacks on failure. This is done my simply adding a --timeout flag to the rig deploy command.
If the rollout does not succeed within the given time, the system will automatically be rolled back to the previous rollout.
rig deploy <capsule-id> --timeout 5m
If you want to disable automatic Rollbacks, but still want to set a timeout, you can use the --no-rollback flag.